Queries - Write and Execute Data Queries
The Queries feature allows you to write, execute, and manage SQL queries against your connected databases. This guide covers the query editor interface, execution options, parameter handling, and special database type considerations.
Accessing Queries
- Navigate to your report in the application
- Click on the Query tab in the report navigation
- Select an existing query or create a new one
Note: The query interface includes tabs for Query, Table, Params, Rendered Query, and Run History.
Query Editor Interface
The query editor adapts based on your database connection type:
AI-Powered Query Generation
PyQueryHub includes an intelligent AI assistant that can generate SQL queries from natural language descriptions:

Using the AI Assistant:
- Click the AI Assist button in the query editor toolbar
- Describe what you want in plain English (e.g., "Show me all users who signed up in the last 7 days")
- The AI will generate a MySQL query based on your database schema and description
- Review and modify the generated query as needed
- Click Generate & Run to execute the query immediately
AI Assistant Features:
- Natural language processing - Understands complex data requests in plain English
- Schema awareness - Uses your actual database structure to generate accurate queries
- MySQL optimization - Generates queries specifically optimized for MySQL syntax
- Context understanding - Interprets relationships between tables and common query patterns
- Instant execution - Generated queries can be run immediately or further customized
Example prompts:
- "Show sales by region for the current month"
- "Find customers who haven't made a purchase in 90 days"
- "Get the top 10 products by revenue this quarter"
- "List all users with incomplete profiles"
SQL Database Connections
For traditional databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, BigQuery, etc.):
- Monaco Code Editor: Full-featured SQL editor with syntax highlighting
- Resizable Layout: Drag the divider to adjust editor/results ratio
- Database Schema Panel: Toggle the right panel to browse tables and columns
- Auto-completion: SQL keywords and database schema suggestions
- Execution Metrics: View query execution time and data size
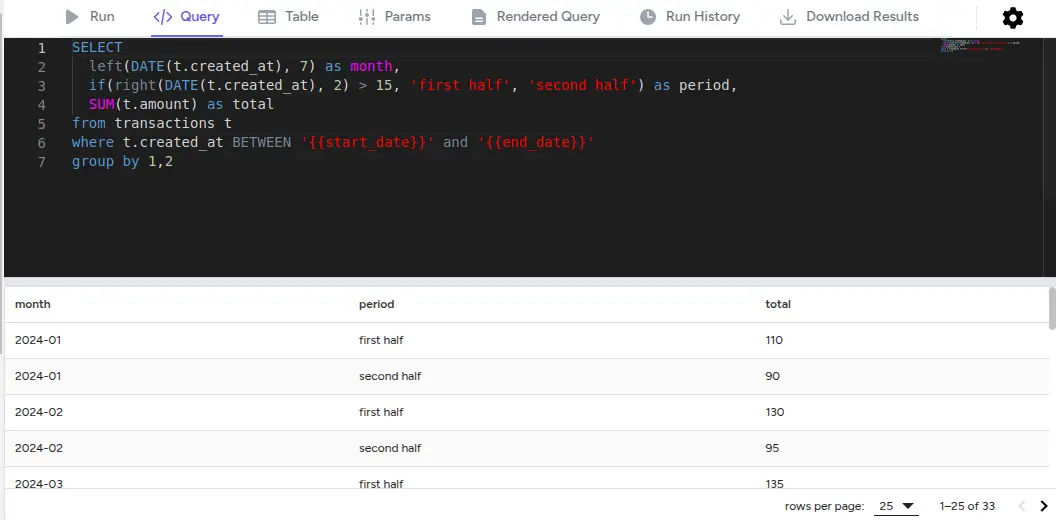
Running SQL Queries:
- Write your SQL in the Monaco editor
- Click the Run button or press Ctrl/Cmd + Enter
- Results appear below with sortable columns
- Execution metrics are displayed (time, data size)
Google Sheets Connections
For Google Sheets connections, the interface is different:
- Spreadsheet Selector: Choose from spreadsheets in your Google Drive
- Sheet Selector: Select the specific sheet/tab within the spreadsheet
- No SQL Editor: Google Sheets don't support SQL queries
- Raw Data Import: The complete sheet data is imported for chart processing
Using Google Sheets:
- Select a spreadsheet from the dropdown
- Choose the specific sheet/tab you want to use
- Data is automatically imported - no query execution needed
- All filtering and processing happens in chart configuration
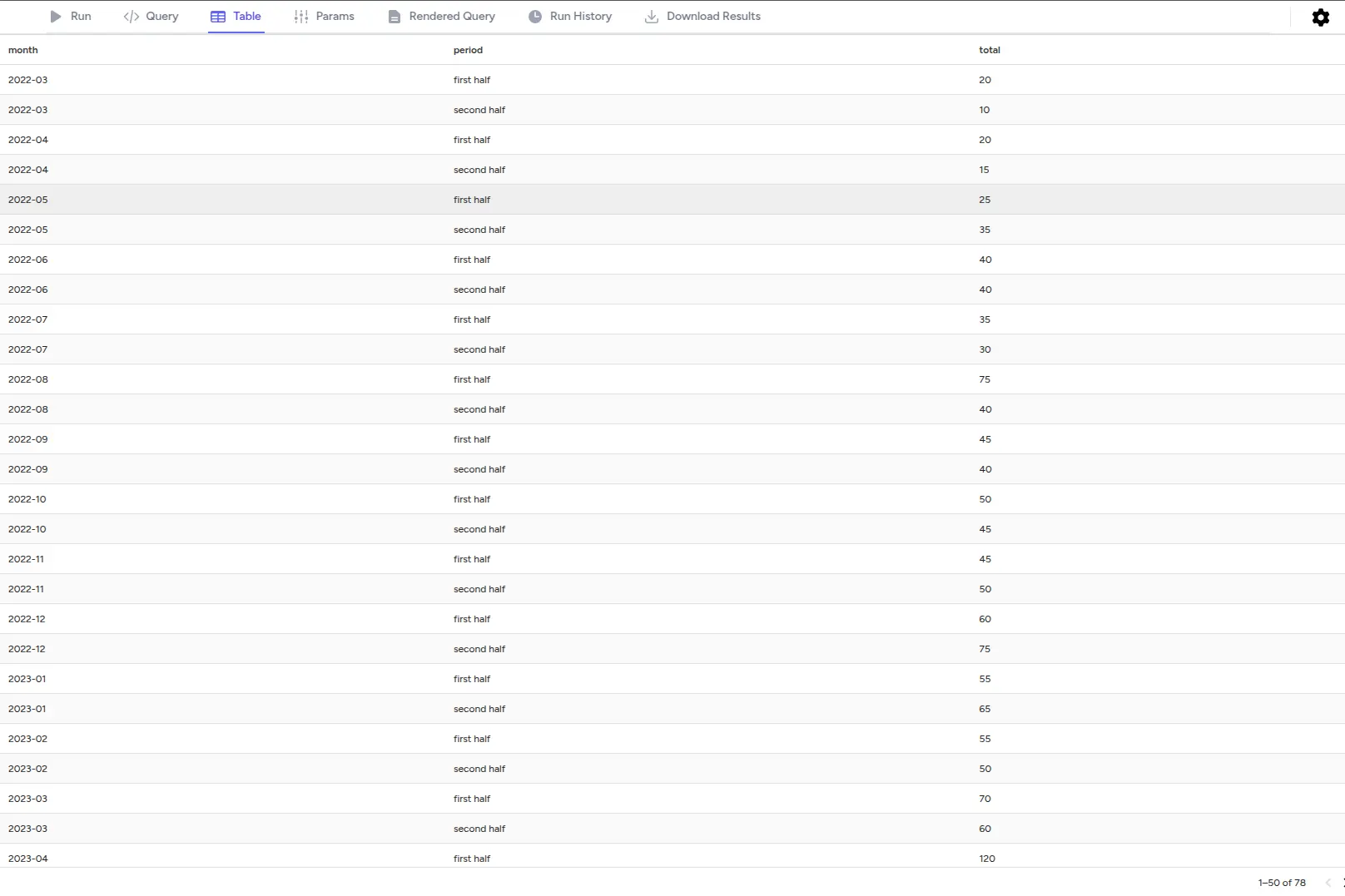
Table Tab
View your last query results in a full-screen table:
- Pagination is fixed to 50 rows per page
- You can sort by any column header
- Full-screen view for detailed data analysis
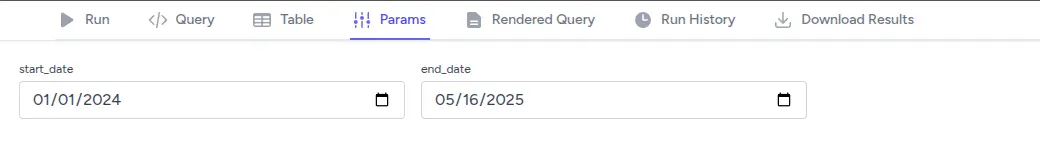
Params Tab
If your query uses parameters (defined in YAML), the Params tab lets you:
- Fill in or adjust parameter values via a form
- Re-run the query with new values to see updated results
- Test different parameter combinations
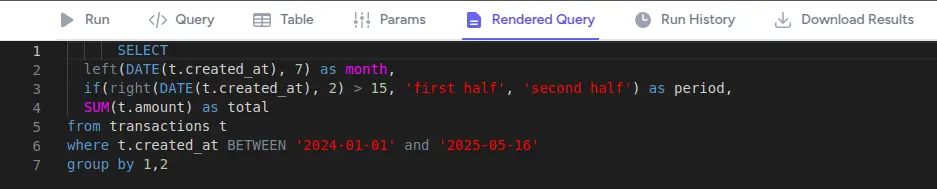
Rendered Query Tab
See the actual SQL sent to the database after Liquid templating:
- Read-only editor showing the final query
- Handy for debugging parameter substitution
- Copy the final statement for external use
Query Options & Schema Panel
Click the panel toggle in the top-right to open/close the Query Options & Schema panel, which includes three main tabs:
Schema Tab
The Schema tab provides powerful database exploration and code injection features:
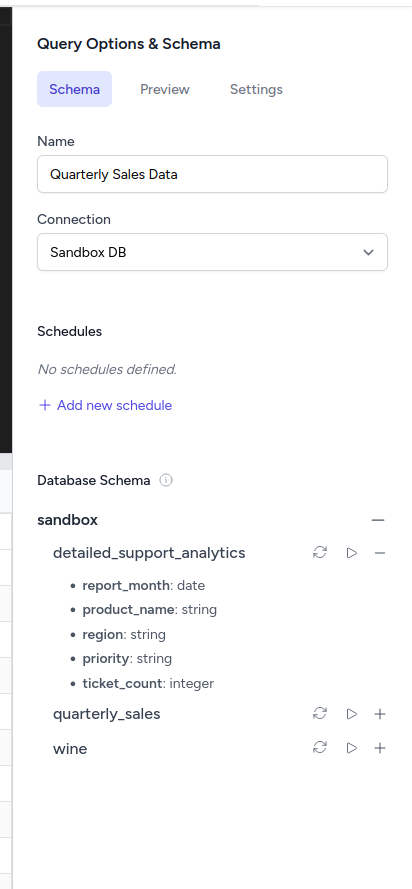
- Database Connection: Switch between your configured database connections via dropdown
- Query Name: Edit and rename your query directly in the panel
- Schema Browser: Expandable tree view of your database structure
- Table Injection: Click the arrow icon (▷) next to any table to inject the table name into your query
- Field Injection: Click individual fields to inject column names into your SQL
- Schema Refresh: Refresh button (🔄) to update the database schema if structure changes
- SQL Preview: Click the expand icon next to tables to inject complete table SQL for preview
Schema Injection Features
The schema panel makes query writing effortless with these injection capabilities:
Table Name Injection:
- Click the ▷ icon next to any table (e.g.,
detailed_support_analytics,quarterly_sales,wine) - Table name gets automatically inserted at your cursor position in the query editor
- Perfect for FROM clauses and JOIN statements
Field Name Injection:
- Expand any table to see its columns with data types
- Click on individual fields (e.g.,
report_month: date,product_name: string) - Field names are injected directly into your query
- Saves typing and prevents column name errors
Schema Refresh:
- Database schema is cached for performance
- Click the refresh icon (🔄) when your database structure changes
- Updates table lists, column names, and data types
- Essential when new tables or columns are added
SQL Preview & Structure:
- Use the preview functionality to see complete table structures
- Inject entire table SQL definitions for reference
- Helpful for understanding data types and constraints
Preview Tab
The Preview tab provides interactive data exploration with automatic table previews:
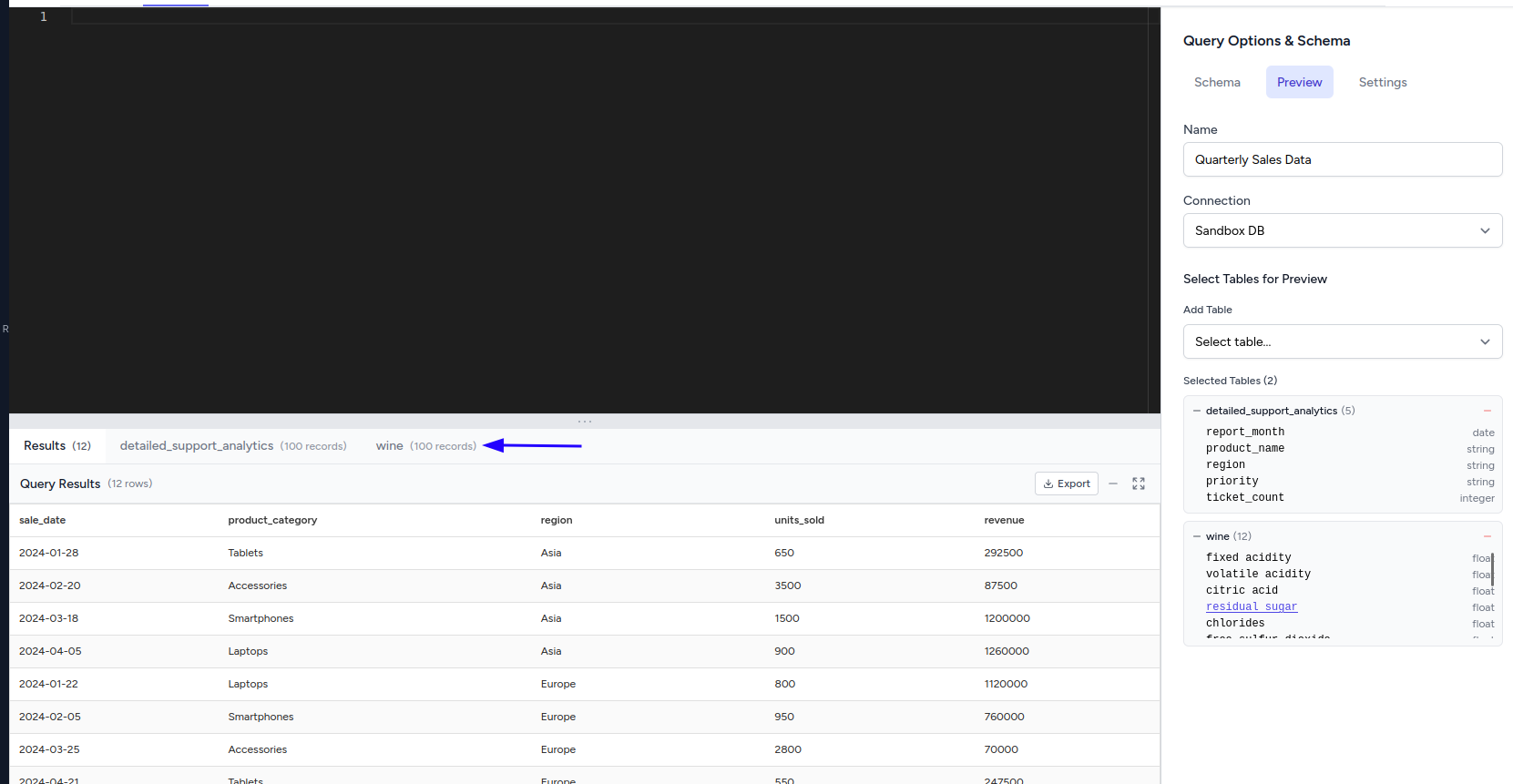
Table Selection & Preview:
- Click on any table in the schema browser to automatically load a 100-record preview
- Table data appears instantly in the Preview tab without running a query
- Perfect for exploring data structure and content before writing SQL
- No need to write
SELECT * FROM table LIMIT 100- it's automatic
Field Name Injection from Preview:
- Click on any column header in the preview to inject the field name into your query
- Field names are inserted at your cursor position in the SQL editor
- Combine with table injection for rapid query building
- Eliminates typing errors and speeds up query development
Data Exploration Workflow:
- Browse tables in the Schema tab
- Click a table name to see preview data in Preview tab
- Click column headers to inject field names into your query
- Use the refresh icon if table structure changes
- Build queries efficiently with visual data reference
This feature makes data exploration intuitive - you can see actual data samples while building your queries, making it easier to understand data types, formats, and content patterns.
Settings Tab
The Settings tab provides comprehensive query editor configuration options:
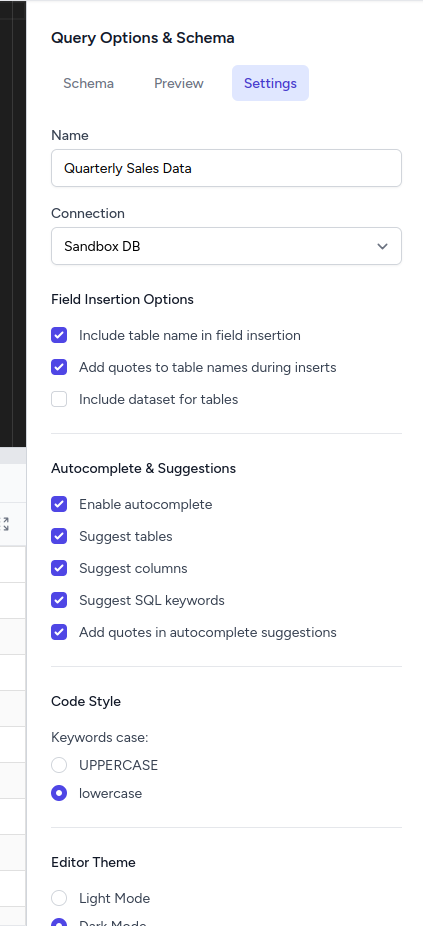
Query Configuration:
- Name: Edit the query name directly in the panel
- Connection: Switch between different database connections via dropdown
Field Insertion Options:
- Include table name in field insertion: When enabled, clicking fields injects
table.columnformat instead of justcolumn - Add quotes to table names during inserts: Automatically wraps table names in backticks when injecting (e.g.,
`table_name`) - Include dataset for tables: For databases like BigQuery, includes the dataset prefix (e.g.,
dataset.table.column)
Autocomplete & Suggestions:
- Enable autocomplete: Turns on/off Monaco editor autocomplete functionality
- Suggest tables: Include table names in autocomplete suggestions
- Suggest columns: Include column names in autocomplete suggestions
- Suggest SQL keywords: Include SQL keywords (SELECT, FROM, WHERE, etc.) in suggestions
- Add quotes in autocomplete suggestions: Automatically add quotes around table/column names in suggestions
Code Style:
- Keywords case: Choose between UPPERCASE or lowercase for SQL keywords
- UPPERCASE: SELECT, FROM, WHERE (traditional SQL style)
- lowercase: select, from, where (modern preference)
Editor Theme:
- Light Mode: Bright editor theme with dark text on light background
- Dark Mode: Dark editor theme with light text on dark background (default)
These settings are saved as browser cookies and persist across sessions. Each setting immediately affects the query editor behavior, allowing you to customize the development experience to match your preferences and coding standards.
AI Query Assistant
PyQueryHub includes an AI-powered query helper:
- Natural Language Prompts: Describe what data you need in plain English
- Query Generation: AI generates SQL based on your database schema and prompt
- Query Refinement: Improve existing queries with AI assistance
- Token Usage Tracking: AI usage is tracked per workspace with quota limits
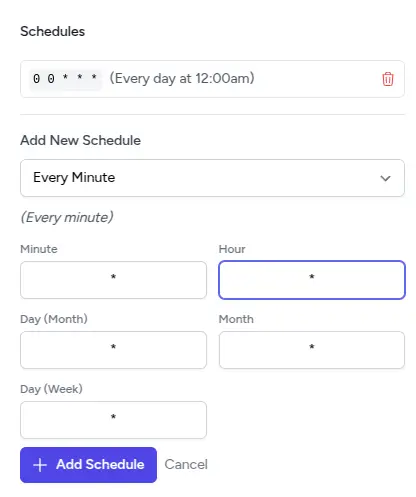
Query Scheduling and Alerts
Queries can be scheduled to run automatically:
- Schedule Configuration: Set up recurring execution times
- Alert Integration: Trigger notifications when query results meet specific conditions
- History Tracking: All scheduled runs are logged with execution details
Query Execution and Results
Execution Methods
- Run Button: Click the Run button in the interface
- Keyboard Shortcut: Press Ctrl/Cmd + Enter to execute
- Selected Text: Execute only the selected portion of your query
- Background Execution: Large queries run asynchronously with progress tracking
Results Display
- Inline Results: Results appear below the editor in the Query tab
- Full-Screen Table: Switch to Table tab for expanded view
- Sortable Columns: Click column headers to sort results
- Pagination: Results are paginated for large datasets
- Export Options: Download results in various formats
Execution Metrics
Each query run provides detailed metrics:
- Execution Time: Query runtime in milliseconds
- Data Size: Size of returned data in bytes
- Row Count: Number of rows returned
- Execution History: Previous runs with timestamps and performance data
Error Handling
- Syntax Errors: SQL syntax issues are highlighted in the editor
- Database Errors: Connection and execution errors are clearly displayed
- Timeout Handling: Long-running queries have appropriate timeout management
- Retry Logic: Failed queries can be easily re-executed
Query Parameters and Templating
Queries support dynamic parameters through Liquid templating:
Parameter System
- YAML Definition: Parameters are defined in YAML format
- Type Support: Text, numbers, dates, dropdowns, and more
- Default Values: Set default values for parameters
- Validation: Parameter validation ensures data integrity
Liquid Templating
PyQueryHub uses Liquid templating for parameter injection:
- Parameter Substitution:
{{ parameter_name }}syntax - Conditional Logic:
@{% if %}statements for dynamic queries - Filters: Apply formatting and transformations
- Assign Statements: Create derived variables
Parameter Interface
- Auto-generated Forms: Parameters create interactive form controls
- Real-time Updates: Change parameter values and re-run queries
- Parameter History: Previous parameter values are saved with query runs
For detailed parameter documentation, see the Params guide.
Query History and Versioning
Run History
- Complete Audit Trail: Every query execution is logged
- Result Storage: Query results are stored for quick retrieval
- Parameter Tracking: Parameter values used for each run are saved
- Performance Metrics: Execution time and data size for each run
Query Versioning
- Original Query Storage: Both original and rendered queries are saved
- Parameter Snapshots: Parameters used for each execution are preserved
- Result Comparison: Compare results across different runs
- History Retrieval: Access previous query versions and results
Database-Specific Features
Traditional SQL Databases
- Full SQL Support: Complete SQL syntax support based on database type
- Schema Introspection: Automatic discovery of tables, columns, and types
- Connection Switching: Change database connections per query
- Performance Optimization: Query execution metrics and optimization suggestions
Google Sheets
- No SQL Interface: Spreadsheet and sheet selection interface
- Real-time Data: Direct connection to live Google Sheets data
- Schema Detection: Automatic column name detection from first row
- Authentication: OAuth-based secure connection to Google Drive
Cloud Data Warehouses
- BigQuery: Support for complex analytical queries
- Redshift: Optimized for large-scale data warehouse operations
- Azure SQL: Enterprise-grade security and performance features
Best Practices
Query Performance
- Use LIMIT clauses: Prevent accidentally returning huge datasets
- Optimize WHERE conditions: Use indexes effectively
- Parameter validation: Validate parameters to prevent SQL injection
- Connection management: Choose appropriate database connections
Code Organization
- Descriptive names: Use clear, meaningful query names
- Comments: Document complex queries with SQL comments
- Parameter documentation: Explain parameter purposes in YAML
- Version control: Use query history to track changes
Security Considerations
- Parameter binding: Always use parameters instead of string concatenation
- Connection isolation: Use appropriate database users with limited permissions
- Data access: Ensure queries only access authorized data
- Audit logging: Monitor query execution and data access patterns
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Connection Errors: Verify database connection settings and credentials
- Timeout Issues: Optimize queries or increase timeout limits
- Permission Errors: Check database user permissions
- Parameter Errors: Validate parameter types and values
Getting Help
- Error Messages: Read error messages carefully for specific guidance
- Query History: Check previous successful runs for reference
- Database Logs: Review database logs for detailed error information
- Support: Contact support with specific error messages and query details
For more information on related features:
- Database Types: Detailed database connection guides
- Params: Parameter system documentation
- Charts: Using query results in visualizations